Turning FBR Mandates into a Structured and Sustainable Compliance Process
With Digital Invoicing now mandatory for multiple sectors under SROs such as 1005(I)/2021, 183(I)/2022, and others, every business falling under FBR’s notified categories must prepare for full integration. Whether it is a retail outlet, a wholesale distributor, a registered service provider, or a manufacturer, the expectation in 2025 is clear: invoices must be digitally issued, submitted to FBR in real time, and carry a valid verification code.
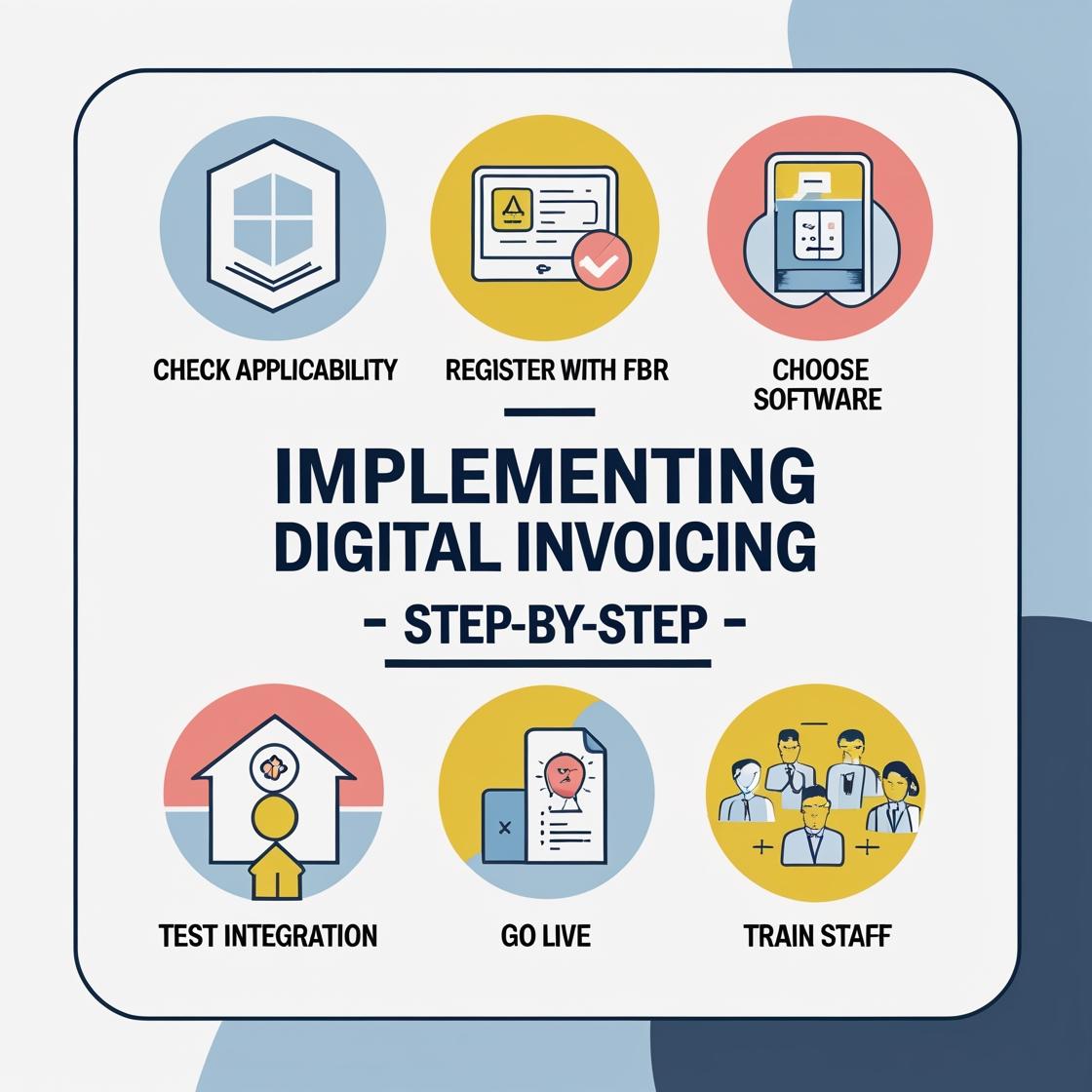
While the requirement may seem technical at first, the actual steps to implement Digital Invoicing are straightforward when approached systematically.
Step 1: Determine Applicability
The first step is for every business to confirm whether Digital Invoicing is currently mandatory in their category. As of 2025, FBR has officially enforced integration on:
-
Tier-1 retailers (per SRO 1005(I)/2021)
-
Wholesalers and distributors of specified sectors (e.g., FMCG, electronics, pharma – under SRO 183(I)/2022)
-
Sales tax–registered service providers
-
Manufacturers of taxable goods
Businesses in these categories are legally required to comply. Others should stay alert, as expansion continues sector by sector.
Step 2: Secure Proper FBR Registration
Before using the Digital Invoicing system, a business must ensure:
-
Registration on FBR’s IRIS portal
-
A valid NTN (National Tax Number) and, where applicable, a Sales Tax Registration Number (STRN)
-
Access to the e-invoice portal and valid digital credentials for integration
 FBR credentials are required to authenticate invoice submission. If any of these components are missing or outdated, integration will not be successful.
FBR credentials are required to authenticate invoice submission. If any of these components are missing or outdated, integration will not be successful.
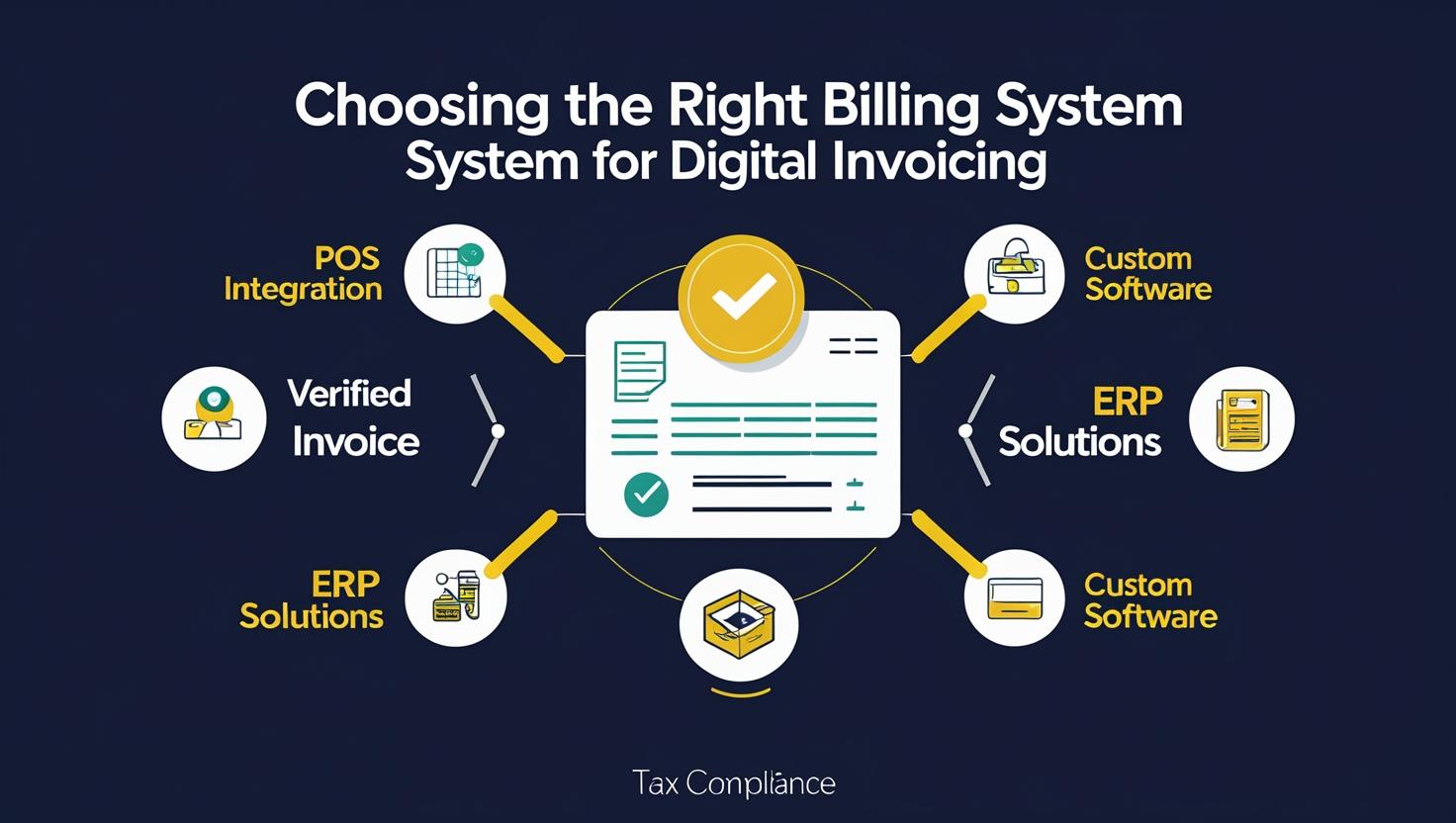
Step 3: Choose or Upgrade the Billing System
Every business must use invoicing software capable of communicating with FBR’s system. There are several ways to do this:
-
FBR-Integrated POS Systems
For retail and physical sales outlets, certified POS providers offer out-of-the-box integration with FBR’s invoice verification system. -
ERP Systems with Invoicing Modules
Businesses using software such as SAP, Oracle, QuickBooks, or Zoho can enable Digital Invoicing by configuring plugins or modules provided by developers. -
Custom Billing Solutions
For businesses with in-house systems, developers can use FBR’s public documentation to enable real-time invoice transmission.
In each case, the goal is to issue a standard-format invoice that is automatically submitted to FBR and returned with an official Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and QR code.
Step 4: Conduct Test Integration
Before live rollout, every business should test its integration in FBR’s sandbox (test environment). This ensures:
-
Invoice formats are correctly generated
-
Required fields (tax, codes, buyer details) are populated
-
System errors are detected before public use
Testing minimizes the risk of invoice rejection and penalties once operations go live.
Step 5: Go Live and Monitor Submissions
After successful testing, the business should begin issuing only FBR-verified invoices. It is essential to:
-
Monitor each transaction to confirm submission and approval
-
Ensure the IRN and QR code are printed on or attached to each invoice
-
Reconcile daily transactions with FBR confirmation logs
 Any invoice issued without FBR verification after going live is considered invalid under the law.
Any invoice issued without FBR verification after going live is considered invalid under the law.
Step 6: Train Staff and Document Workflow
Smooth implementation requires that staff responsible for invoicing:
-
Understand the submission process
-
Know how to respond to system errors
-
Maintain backups and error logs
-
Follow a defined workflow that ensures compliance at all points of sale
Incorporating these practices ensures internal accountability and simplifies tax return filing, especially during audits.
How CABCS Can Help
CABCS helps every business plan, test, and fully implement FBR-compliant Digital Invoicing. We support system selection, credential registration, POS and ERP configuration, and post-launch monitoring — ensuring that compliance is not just achieved, but sustained.