A Clear Explanation of How Every Business Connects to FBR’s System in 2025
Digital Invoicing, as introduced by the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), is designed to ensure that every business’s taxable sales are reported to FBR at the time of transaction. It is a central tool in Pakistan’s shift toward real-time tax enforcement and data-driven compliance.
Although it was initially introduced under SRO 1005(I)/2021 for Tier-1 retailers, later policy updates and SROs in 2022, 2023, and 2024 have steadily extended its reach. As a result, Digital Invoicing is now required in many sectors — and understanding how the system works is essential for all business owners, regardless of technical background.
This section provides a clear explanation of how Digital Invoicing operates in practice.
What Happens When a Business Issues a Verified Invoice?
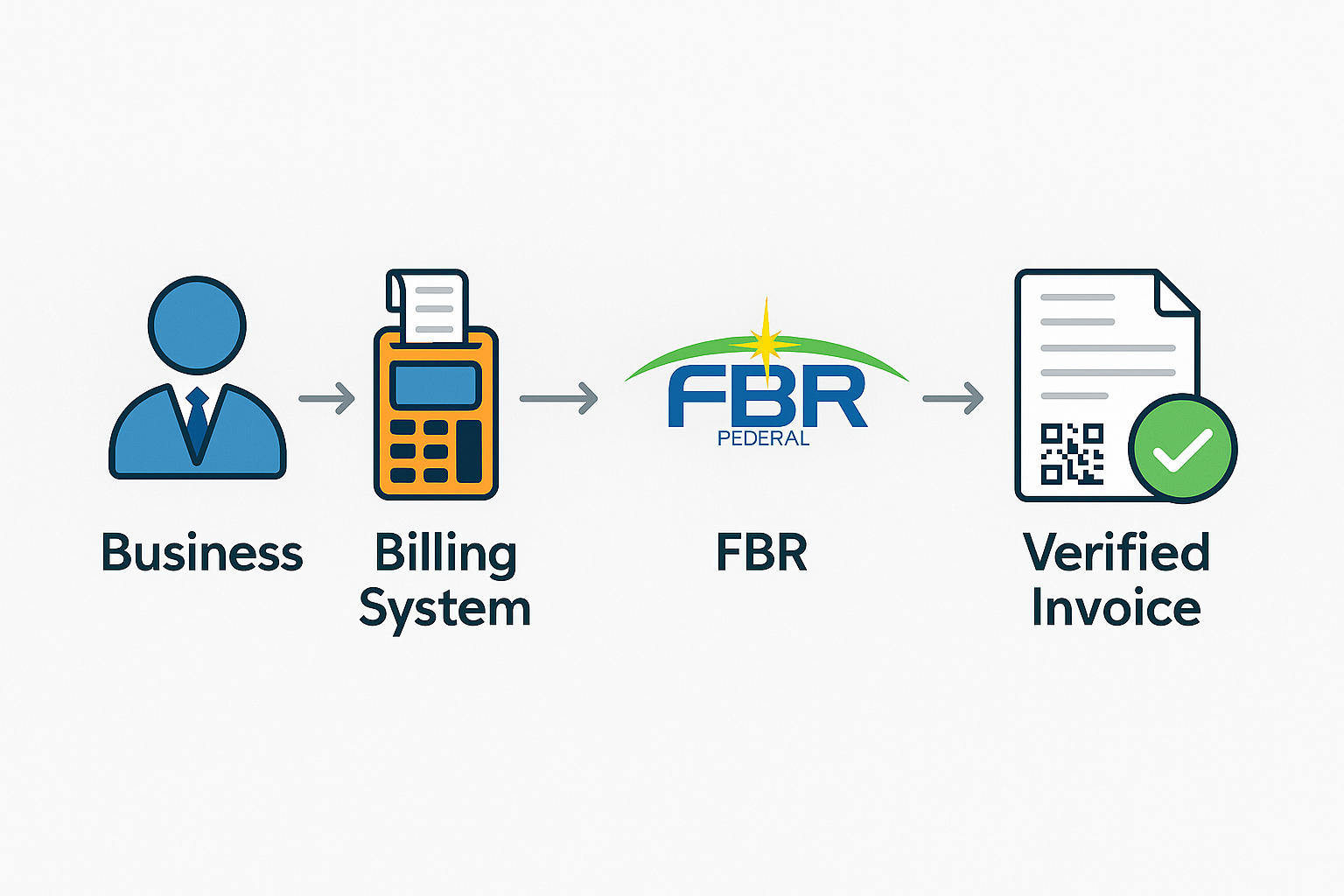
The Digital Invoicing process starts when a business creates an invoice through a compliant billing system. This could be a Point of Sale (POS) device, enterprise software (ERP), or cloud-based billing tool.
Once an invoice is generated:
- The billing system sends the invoice data directly to FBR in real time.
- FBR’s system validates the information — including sales tax, seller registration, and invoice structure.
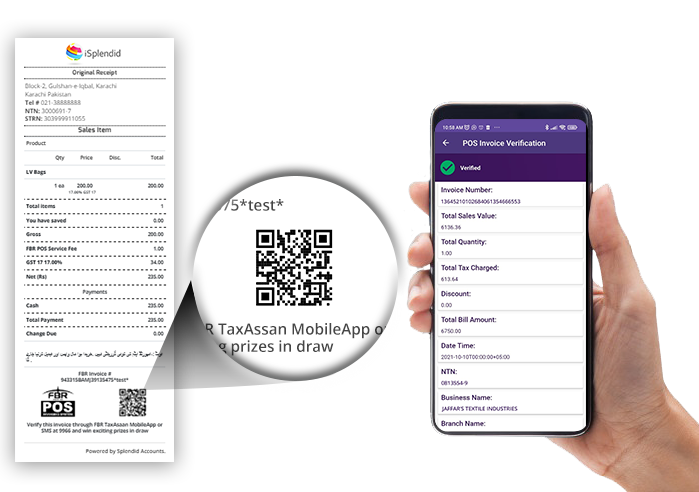
- If approved, FBR returns an Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and a QR code.
- The verified invoice, now containing the IRN and QR code, is issued to the customer.
 The entire process typically takes only a few seconds and requires no manual intervention after setup.
The entire process typically takes only a few seconds and requires no manual intervention after setup.
Key Components of the Process
- Invoice Generation
Every business uses its system to input transaction details — such as buyer and seller names, sales items, quantities, and applicable taxes. - System Integration
The software must be integrated with FBR’s digital infrastructure. This can be done using certified software providers or through ERP modules that are adapted for compliance with SRO-defined technical formats. - FBR Validation
FBR checks the invoice to ensure it meets formatting, tax calculation, and registration requirements. This ensures uniformity and prevents errors or manipulation. - Invoice Confirmation and QR Code
Upon successful validation, FBR issues an IRN and a unique QR code. These act as proof that the invoice is recorded in the national tax system. - Final Invoice Delivery
The business provides the invoice to the customer — either printed or digital — with the IRN and QR code visible. This confirms its status as an official, FBR-recognized tax invoice.
 What This Means for Every Business
What This Means for Every Business
Whether issuing 10 invoices per day or hundreds, every business falling under the SRO guidelines must ensure that each invoice is:
- Sent to FBR immediately upon generation
- Verified and digitally stamped
- Issued only after receiving the official confirmation
This not only supports regulatory compliance but also eliminates inconsistencies in recordkeeping and simplifies future tax filings.
Compatibility with Existing Business Tools
FBR has released technical documentation to support integration with:
- POS machines
- Desktop and cloud billing software
- ERP platforms like SAP, Oracle, QuickBooks, and custom solutions
Most modern tools are already compatible or can be made compliant with minimal effort. Businesses should consult their software vendors or tax advisors to ensure compatibility and proper setup.
How CABCS Can Help
CABCS assists every business in setting up a fully compliant Digital Invoicing system, including system integration, staff onboarding, and ongoing support. We also help identify whether your business falls under SRO requirements and ensure smooth communication with FBR’s technical infrastructure.

